Screening of σ2 Receptor Ligands and In Vivo Evaluation of 11C‐Labeled 6,7-Dimethoxy-2-[4-(4-methoxyphenyl)butan-2-yl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline for Potential Use as a σ2 Receptor Brain PET Tracer
Research question
The σ2 receptors are associated with various neurobiological effects, such as intracellular calcium, dopaminergic activity, addiction, neuroprotection, schizophrenia, anxiety and depression. Therefore, the receptor is considered a potential therapeutic target for CNS disorders
The aim of the current study is to identify a new compound that could serve as a σ2 receptor radiotracer for CNS imaging studies.
Experiment
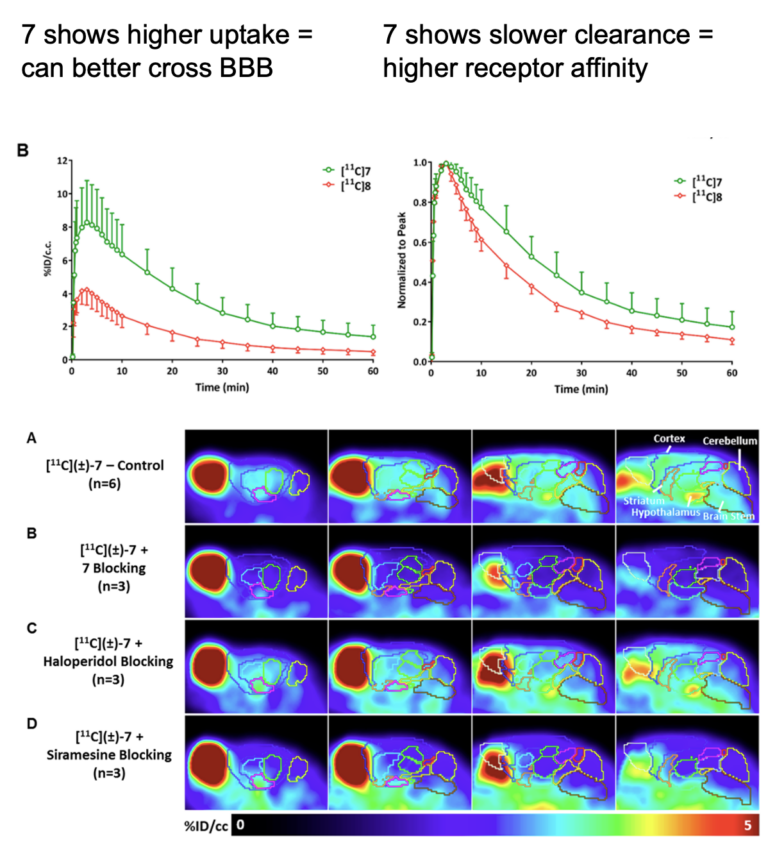
In this study, a panel of 46 compounds containing five different scaffolds known to have high σ2 receptor affinity were screened. 6,7-Dimethoxy-2-[4-(4-methoxyphenyl)butan-2-yl]- 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline [(±)-7] and its desmethyl analogue, (±)-8, showed excellent binding affinity and subtype selectivity for σ2 receptors in vitro. In PET studies (60 min dynamic PET scans), the peak brain uptake of [11C]-(±)-7 was higher than that of [11C]-(±)-8 with specific distribution in the cortex and hypothalamus. Brain uptake or tissue binding was selectively inhibited by ligands with different σ2 receptor binding affinities.
Results
It was demonstrated that PET imaging is an ideal tool for compound screening. In this example, PET delivers information on BBB crossing functionality and receptor affinity. The results suggest [11C]-(±)-7 can be used as a PET radiotracer for imaging the function of σ2 receptors in central nervous system disorders.